The concept of harnessing the power of the sun is a familiar concept and one that has been around since humans have walked the Earth.
Who Invented Solar Panels?
As you will see in our infographic timeline below there were many notable inventors and scientists that made significant progress in the development of Solar Panels. Perhaps the most notable invention came as far back as 1839 from a 19-year-old Frenchman called Edmund Becquerel. He discovered what is called the photovoltaic effect, the underlying scientific process behind the solar cell, while experimenting with a couple of metal electrodes. His process was refined over the following decades by pioneering scientists, and in 1923 Albert Einstein received the Nobel Prize for his theories explaining the photoelectric effect.
In the early 1950s the first uses were made of the photovoltaic cell, sometimes referred to as PV cells. These cells are produced from extremely thin wafers of silicon. These are the types of solar panels that you hear about most frequently these days.
Solar energy has come a very long way since 1958 when the first solar powered satellite was launched. With the recent advent of nanotechnologies, the efficiencies of the PV cell are now many times what they used to be. Now it takes far less roof space, and far less expense, to fully solar power an average home.
Compare quotes from up to 7 installers in your area now.
A Full Timeline History of the Development of Solar Power
| 3rd Century B.C. | Romans and Greeks used mirrors to focus sunlight on torches to light them for religious ceremonies |  |
| 212 B.C. | Similar to the Greeks and Romans, the Chinese documented the use of burning mirrors to light torches for religious purposes |  |
| 20 A.D. | Similar to the Greeks and Romans, the Chinese documented the use of burning mirrors to light torches for religious purposes |  |
| 1st to 6th Century A.D. | The popularity of using ‘sun rooms’ to let in the sun’s warmth increased particularly in the Roman Empire |  |
| 13th Century A.D. | The Anasazi in North America live in south-facing cliff dwellings that capture the winter sunlight for heat |  |
| 1767 | Horace Bénédict de Saussure, a swiss scientist, is credited with builidng the worlds first solar oven capable of reaching 110 °C – a insulated box with three layers of glass design to trap outgoing thermal radiation |  |
| 1839 | A 19-year-old Frenchman called Edmund Becquerel, discovered what is called the photovoltaic effect, the physics behind the solar cell, while experimenting with a couple of metal electrodes. | 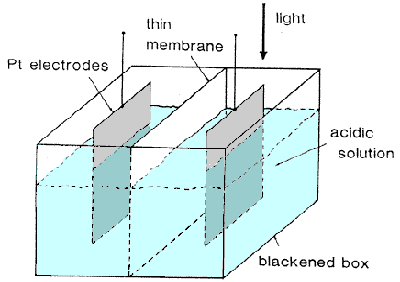 |
| 1860s | French mathematician Augustin Mouchot was perhaps the first to look for an energy replacement to coal which he believed would eventually run out. Mouchot invented the solar steam engines using a parabolic dish to concentrate solar energy on a water reservoir. | 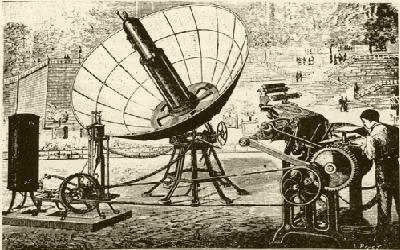 |
| 1873 | English electrical engineer, Willoughby Smith published an article describing the photoconductivity of Selenium (leading to the invention of photoelectric cells) |  |
| 1876 | Englishmen, William Grylls Adams and Richard Evans Day discovered lighting a junction between selenium and platinum has a photovoltaic effect – the first demonstration that light can produce electricity |  |
| 1883 | American inventor, Charles Fritts creates the first solar cells from wafers of selenium |  |
| 1891 | Clarence Kemp invented and patented (in USA) the passive solar water heater | 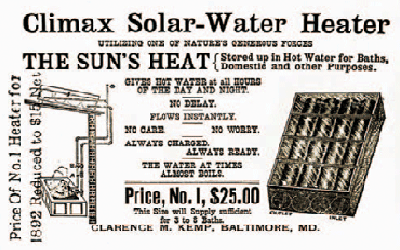 |
| 1914 | American physicist Robert Andrews Millikan provides experimental proof of the photoelectric effect as described by Albert Einstein in 1905 |  |
| 1921 | Albert Einstein wins the Nobel Prize for his research dating back to 1900 and technical paper explaining the photoelectric effect |  |
| 1932 | Audobert and Stora discovered a Photovoltaic Effect in cadmium sulfide (CdS) | 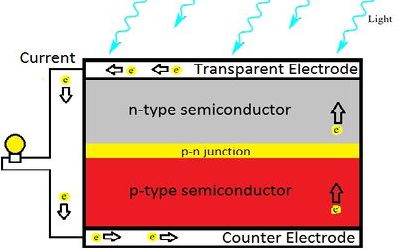 |
| 1953 | American professor, Dan Trivich was the first to make theoretical calculations on the efficiency of solar cell using different materials |  |
| 1954 | Bell Labs invent first solar cell with 4% efficiency – the first with sufficient efficiency to run everyday equipment |  |
| 1950s | Western Electric commenced selling licenses for solar-powered technologies such as dollar bill changers and solar powered punch card decoders |  |
| 1957 | Hoffman Electronics creates photovoltaic cells with 8% efficiency and then one year later in 1958 achieves 9% efficiency and 14% in 1960 |  |
| 1958 | Solar is successfully used in space via the Vangua I space satellite to power radios. Solar eventually became the accepted source of power for space applications and that still remains the case. |  |
| 1963 | Japan installs 242W solar array on a lighthouse – the world’s largest solar array at the time. |  |
| 1970s | NASA after years of research and development of space Solar PV systems dedicates a 3.5kW solar system to the Papago Indian Reservation which powers water pumps and electricity in 15 homes. |  |
| 1981 | Paul MacCready creates the first solar aircraft and travels across the English Channel using only solar power and the wind. |  |
| 1982 | Australian, Hans Tholstrup, made the first transcontinental journey on a solar powered car which he called “The Quiet Achiever”. He later devised the concept of the World Solar Challenge. |  |
| 1983 | The global production of solar photovoltaics exceeds 21MW – with ARCO building a 6MW solar plant in central California |  |
| 1985 | The University of New South Wales sets the record for silicon solar efficiency in Solar PV breaking the 20% barrier |  |
| 1993 | Pacific Gas and Electrical develops the first grid-supported, distributed power plant to reinforce a weak feeder. |  |
| 1998 | Subhendu Guha invented a flexible solar roofing material utilising amorphouse silicon as the total cumulated global installed solar approaches 1GW |  |
| 2001 | The John Howard Australian Government introduced a Renewable Energy Target (MRET) with ambition of reaching 20% renewable by 2020. |  |
| 2008 – 2013 | In 2008 to 2009 many states of Australia introduced feed-in-tariff schemes to incentivise Australians to install residential solar systems. The schemes led the initiated the solar boom in Australia and the schemes were wound back progressively over 2011 to 2013 |  |
| 2018 | Australian installed 1.6GW of solar increasing from 1.1GW in 2017 and 600MW in 2016. Market growth driven by rapidly declining price of solar while electricity costs are rising. | 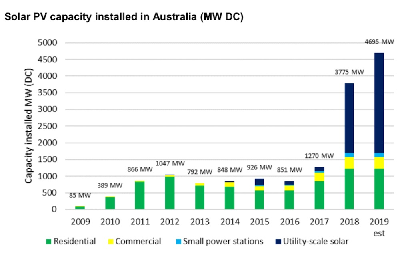 |
- Why a big battery could be cheaper than a small battery with the federal rebate? - 19 June, 2025
- Heat Pump Costs – Solar Choice Price Index - 1 June, 2025
- Solar Panel Costs: Solar Choice Price Index | July 2025 - 1 June, 2025
