As interest in solar battery storage grows, so does the number of people with questions about their many options. At some point, energy storage system shoppers may find themselves having to decide between AC battery storage or DC battery storage. (N.B. These two approaches are more accurately referred to as AC-coupled battery storage and DC-coupled battery storage, but for the purposes of this article, we will abbreviate them to AC and DC storage.)
What is the difference between AC and DC battery storage, and what are the relative advantages and disadvantages of each?
Compare solar and battery quotes online now.
About DC and AC Electricity
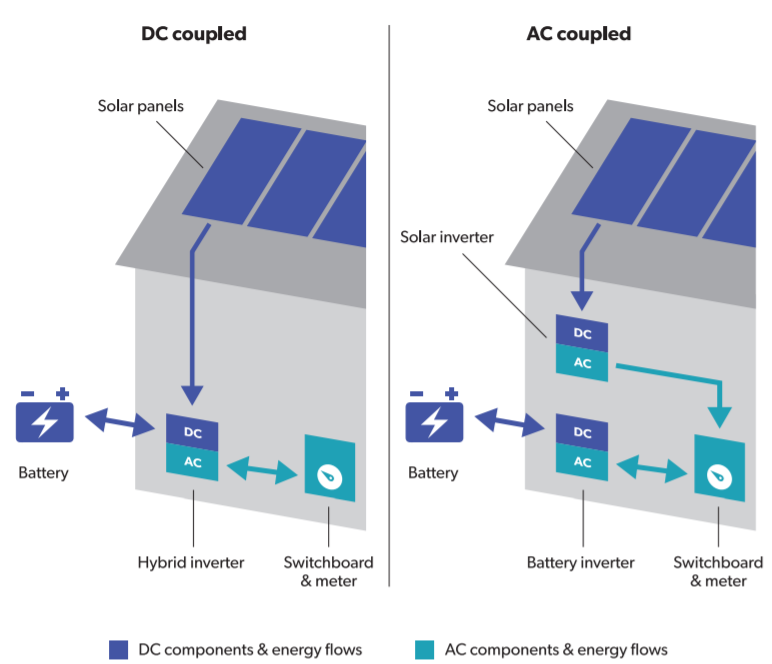
Direct current (DC) electricity is what solar panels produce and what batteries hold in storage while alternating current (AC) electricity is the type used on the grid and in most household devices. A device called an inverter is required to convert the DC electricity from solar panels into appliance-friendly AC.
Batteries likewise require an inverter to render their stored energy useable. If they are DC-coupled, they can share the inverter with the solar panels, while if they are AC-coupled, they’ll require a separate inverter of their own.
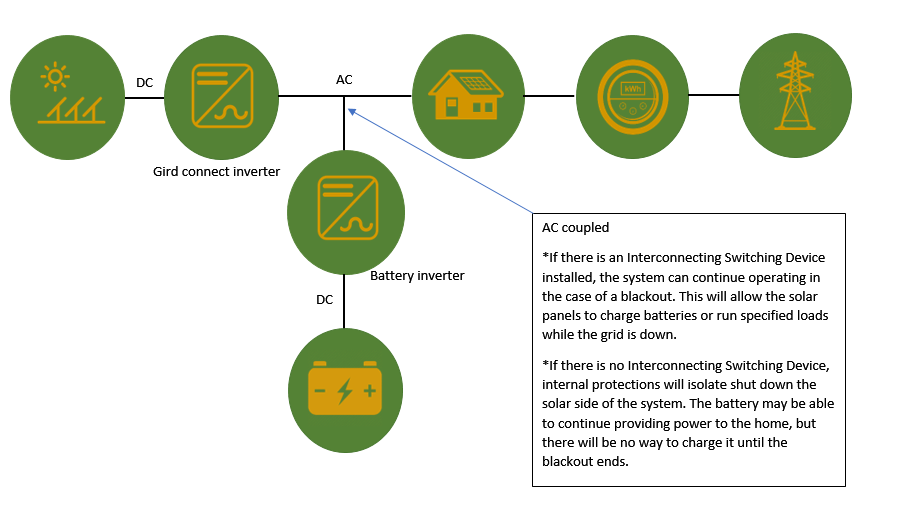
What Is An AC-Coupled Solar Battery?
An AC-coupled storage system is connected to the AC grid mains that service the property (that is, the lines coming in from the street).. You can think of this type of arrangement as a ‘two box’ solution – because there is one ‘box’ (inverter) for the solar panels, and another for the battery bank.
The main advantage of AC-coupled battery storage is that it is the easiest and generally more cost-effective way to retrofit batteries onto a pre-existing solar PV system.
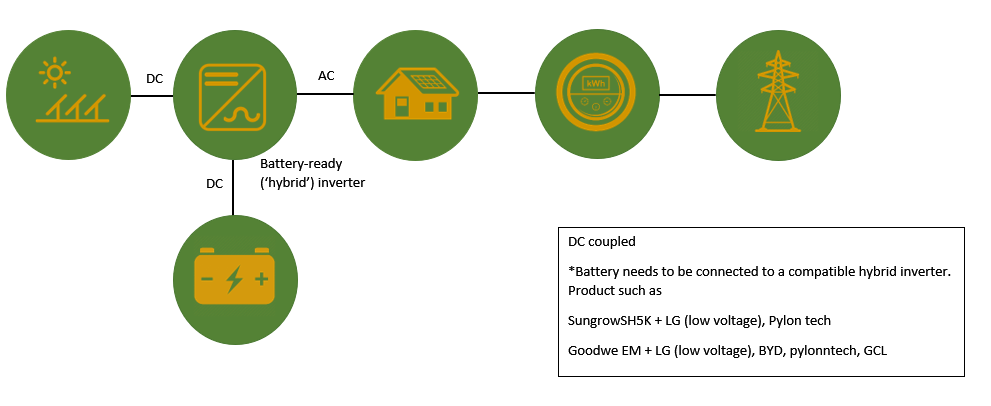
What Is A DC-Coupled Solar Battery?
A DC-connected energy storage system connects to the grid mains at the same place as the solar panels; this usually means that they share a ‘hybrid’ inverter. You can think of this as a ‘one box’ solution, because there is only one inverter instead of two.
Because they contain fewer components (which usually translates into lower costs), we generally recommend DC-coupled systems for homes considering a brand new solar & storage system (as opposed to a retrofit). Having a single inverter also allows households to get around local network capacity restrictions, which can be prohibitively small in some areas (most notably, South Australia, where the limit is 5kW for single phase grid connections).
Example diagram of a solar PV system with DC-coupled battery storage. (Click to enlarge.)
Which One Is Right For You?
Generally speaking a DC-coupled solar battery will be more efficient and a cheaper option to have installed if you are installing a fresh solar and battery system. If you have an existing solar system and you are looking to add or retrofit a battery, it is likely that an AC-coupled battery will be your best option.
Compare solar and battery quotes online now.
Pros and Cons of AC Coupled vs DC Coupled Batteries
| Feature | AC-Coupled Battery | DC-Coupled Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | ||
| Retrofit Friendly | Easy to add to existing solar systems | Typically requires a new hybrid inverter |
| Flexibility | Works independently of the solar inverter, so you can select from a range of brands | Generally the solar battery must be the same brand as the hybrid solar inverter |
| Redundancy | Separate inverter can be a backup if the main inverter fails | Shared inverter means single point of failure |
| Cons | ||
| Efficiency | Loses energy converting DC to AC and back again | More efficient with fewer energy conversions |
| Cost | Slightly higher cost due to separate inverters | Cheaper option for new solar and battery installations |