In a major boost to the growing market for grid and renewable energy storage, Japanese PV manufacturer, Sharp, has recently debuted a new grid connect energy storage solution dubbed ‘SmartStorage’.
Aimed at commercial and industrial users, the system is designed to reduce peak demand through the use of a lithium-ion battery storage system, thereby minimizing demand charges and electricity usage for large consumers. The system has been introduced in California and is scheduled to be rolled out in the rest of the US over the course of the year.
At the core of the SmartStorage system is a 40kWh lithium-ion battery system (a larger 80kWh system is also available) and a 30kW battery converter/inverter system from Ideal Power. The battery charges at night or during off-peak hours and selectively releases up to 30kW of power as needed when large spikes in electricity consumption occur.
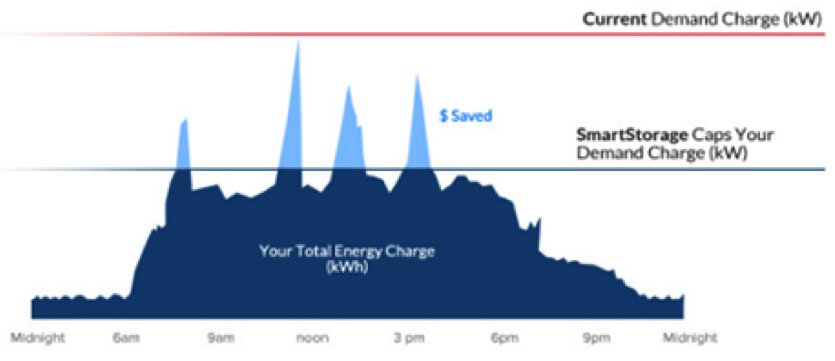
Thus, the system effectively caps peak electrical consumption from the grid. This is particularly attractive for industrial and commercial consumers, who are charged not only for their total energy usage but are also charged a ‘demand charge’ for the maximum peak power they require. The graphic below shows how a storage system could help reduce demand charges.
Image source: Sharp SmartStorage
The SmartStorage system, which has an impressive 10-year service warranty, also employs automated predictive controls and monitoring features to manage the release of energy depending on site conditions and utility rates, maximising value for consumers.
The system is also designed to operate in conjunction with solar PV systems, which could further reduce electricity usage for commercial users. In fact, Sharp is hoping the product will indirectly encourage the growth of solar PV installations. Carl Mansfield, general manager of Sharp’s energy storage division clarifies: “We believe that this product does open up new customers who are interested in solar who would not buy standalone solar.”
“This is not an effort to sell more solar, but it’s very complementary to solar,” he added.
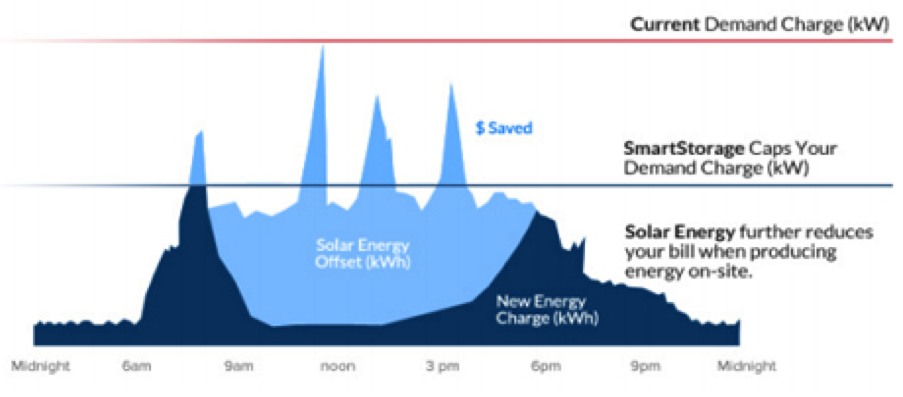
The potential of a combined PV-storage solution in reducing electricity bills for large consumers is highlighted in the graphic below:
Image source: Sharp SmartStorage
Sharp’s expertise in electronics, renewables and batteries provides the company a strong footing to enter the energy storage market. Moreover, as a major PV panel manufacturer, the introduction of an energy storage product is a very strategic move into a complementary market.
In addition to drawing attention to this growing market, Sharp’s entry into energy storage seems to highlight another important trend in the renewables industry – vertical integration and diversification.
Being vertically integrated in the PV space may be critical to entering a nascent market such as energy storage due to the potential to absorb risks and drive down costs. This is evident from moves from other major vertically integrated PV manufacturers such as SunPower and Kyocera entering the storage business as well as big solar installation and energy storage players like SolarCity moving further upstream into PV panel manufacturing.
But fundamentally, all these cases highlight the role power storage has in enabling solar PV to reach its true potential as a reliable and sustainable energy source. It will be interesting to see how exactly this occurs in various world markets, including Australia.
Top Image Credit: Sharp SmartStorage
© 2014 Solar Choice Pty Ltd
- Future of Utilities – Part 1: The death of base-load generators - 11 September, 2014
- Sharp enters energy storage market with SmartStorage - 18 August, 2014
- Phinergy extends electric car range with metal-air battery technology - 13 August, 2014