Are you thinking about adding solar panels to your home? Before making the switch, it’s important to understand how they work, the costs involved, and the best solar system for your needs. Many homeowners feel unsure about the process—but it’s simpler than you think.
This guide breaks down home solar systems, covering installation options, pricing, payback periods and the pro’s & cons involved. By the end, you’ll know what to expect from a residential solar system and how solar electricity can help lower your power bill.
Solar energy is now a mainstream solution,. According to data from the Australian PV Institute over 50% of homes in Queensland and South Australia now have solar panel systems installed. Homeowners nationwide are cutting electricity costs and helping create a more sustainable, eco-friendly future.
Key Takeaways: Quick Guide To Solar Systems for Homes
- How Solar Works: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which an inverter makes usable. Excess energy is stored in a battery or exported to the grid for credits.
- Types of Solar Systems: Choose from grid-connected, off-grid, or hybrid.
- Solar System Size & Savings: A 6.6kW solar system produces 22–25 kWh per day, reducing electricity bills by 40–70%. Homeowners save $1,500–$2,000 per year, depending on a number of factors such as electricity usage and location.
- Solar Battery Storage: A 10kWh battery increases self-consumption to 80–90%, reducing grid reliance. However, batteries increase costs significantly.
- Payback Periods: A 6.6kW solar system pays for itself in 3–5 years, while a solar + battery system extends to 7–10 years due to upfront costs and feed-in tariff reductions.
- Choosing High-Quality Solar Panels: Prioritize high-efficiency panels (21%+), strong warranties (25+ years performance, 10–15 years product), and Tier 1 manufacturers to maximize long-term savings and reliability.
- Finding a Trusted Installer: Choose a CEC-accredited installer with 5+ years of experience, strong customer reviews, clear warranty policies, and local Australian support.
- Hidden Costs & Upgrades: Some homes require switchboard upgrades, tilt frames for south-facing roofs, or extra costs for tile/Kliplok roofing.
- Maximizing ROI: As feed-in tariffs decrease, self-consuming solar power is key. Use timers on hot water systems, dishwashers, and pool pumps to optimize savings.
- Future-Proofing Your System: If planning to add EV chargers, electric heating/cooling, or expand your system, ensure your inverter and roof space support future upgrades.
- Government Rebates & Incentives: The Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES) reduces upfront costs by 30–35%, but rebates decrease annually. Check your state & local incentives before purchasing a solar system.
- Beware of Cheap Solar Systems: Low-cost deals often mean poor installation, weak warranties, and lower long-term performance. Choose quality over price for maximum savings and reliability.
The above only scratches the surface of what you need to know. Keep reading below to understand the most important factors in solar for homes in Australia.
How Do Solar Power Systems Work in Australia?
Understanding how a home solar system works is key to making an informed decision about installing solar panels.
At its core, a solar system converts sunlight into electricity that powers your home. This energy flow starts from your homes rooftop solar panels and moves through an inverter to your home appliances and then to a solar battery or the power grid.
Solar Electricity for Homes
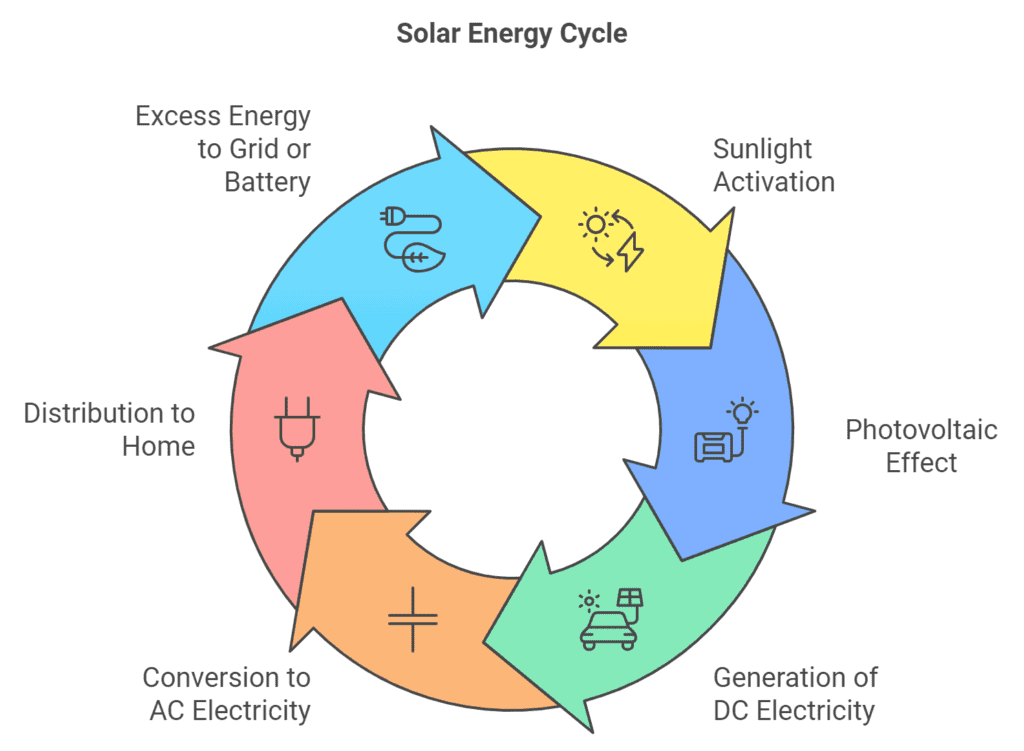
Solar electricity transforms sunlight into usable power through a streamlined process involving solar panels, inverters, and solar batteries:
- Solar Panels: Captures sunlight and converts it to direct current (DC) electricity.
- Inverter: Transforms the electricity from DC power to alternating current (AC) power for home use.
- Solar Battery: Stores excess electricity for later use, reducing your reliance on the grid. This part of the solar system is optional and can be added later down the track.
Key Benefits of Solar Electricity for your home
- Reduce bills: decreases electricity costs by utilising free solar energy during peak daylight hours and selling surplus power back to the grid.
- Sustainability: Offers a clean, renewable energy source that decreases reliance on fossil fuels.
- Reliability: With the inclusion of a solar batteries, a home solar system can provide backup power during power outages.
- Higher Property Value: Homes with solar panel installations often have higher resale value.
For a far more detailed, step-by-step explanation visit our dedicated solar energy page on how residential solar systems work.
Most home solar panel systems in Australia are grid-connected, meaning they work in conjunction with the electrical grid. Below, we break down the three main types of solar for home systems.
Compare quotes from up to 7 installers in your area now.
Types of Solar System
Grid-connected Solar Systems
Your inverter will work with grid power to use all solar power first before drawing any additional power requirements from the grid.
The grid harmoniously supplies power that solar cannot provide at night times (and when it’s cloudy).
Grid-connected solar systems also enable you to sell power back to the grid.
Off-grid Solar Systems
Standalone power systems (or off-grid systems) include solar panels and solar batteries to provide a 24-hour power solution and do not require any grid connection.
Off-grid systems are most common in new construction projects in rural parts of Australia.
Remote properties can often be quoted in excess of $50,000 solely to establish a connection to the power grid.
In these scenarios, it can be economically and environmentally a better choice to put in an off-grid solar system.
Whilst off-grid systems have a much larger upfront cost (usually min. $25,000), you can completely eliminate your power bill.
Hybrid Solar Systems
Hybrid solar systems are grid connected solar systems that include a solar battery to store solar energy.
This energy can then be reused at times when there is no solar power (i.e. night-time).
Solar batteries also provide an excellent backup power source during a power outage and the ability to make greater use of your solar power.
In most cases, including a solar battery will lengthen the payback period of your project due to their high upfront cost. See our deep dive on the financial return of solar batteries.
Is Your Home Suitable for Solar?
- Roof Condition: Ensure your roof is in good condition. Solar panels are designed to last for 25 years and removing them to repair your roof can be costly.
- Roof Orientation: In the southern hemisphere north-facing roof space is optimal for most solar production. However East-facing panels produce more power in the morning and West-facing produce more in the evenings. Generally south-facing roof-spaces require tilt frames to improve their production.
- Shading: Shaded roofs reduce energy output. To maintain optimal production roofs with partial shading should consider micro-inverters or power optimisers.
- Roof Space: You will normally require at least 20 square metres of usable roof space to install an entry level 3kW solar system.
- Electrical Safety: Your home’s wiring and switchboards should be up to code. A qualified installer will ensure it’s safe for solar.
What Size Solar System Do I Need For My Home?
Choosing the right size solar system for your home is crucial for maximizing your return on investment and energy savings. To determine the best size for your needs, it’s important to understand your home’s daily energy consumption and how solar panels can meet that demand during peak sunlight hours.
Understanding Your Home’s Energy Usage
Every household’s energy needs are different, but as a general rule, the average Australian home uses around 20 kWh per day. By matching your solar system size to your daytime energy usage, you can significantly reduce your reliance on the grid and lower your electricity bill.
Using a 6 kW system, for instance, can help a typical home offset up to 40% of its energy needs. If more energy is used during daylight hours, the same system can cover up to 64% of your electricity usage.
View solar system prices on an online quote comparison now
Best Solar System Sizes for Different Homes
- 1-2 bedroom house: A 3kW to 4kW system is generally sufficient for smaller homes. This size is ideal for households that use less electricity or have fewer occupants. It covers basic energy needs such as lighting, small appliances, and daytime power usage.
- 3-4 bedroom house: A 5kW to 6.6kW system is typically perfect for medium-sized homes. This system size can cover a significant portion of your electricity usage, especially if your household consumes energy during daylight hours.
- Larger homes or homes with higher electricity usage: For larger homes or if your household uses more electricity (e.g., working from home, using electric heating/cooling), a 7kW to 10kW system may be more appropriate. This is particularly recommended if you’re considering adding future energy-intensive appliances, like electric vehicles, air conditioning, or a pool heater.
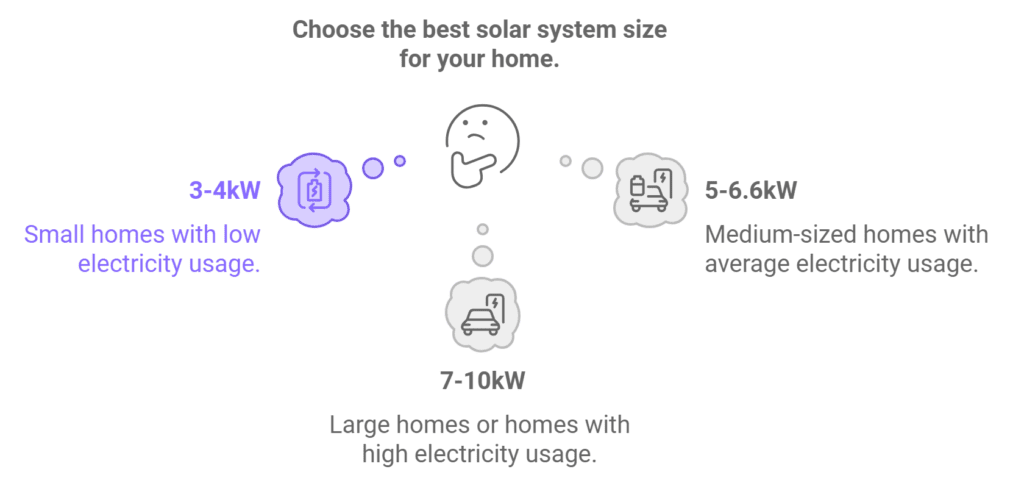
Choosing the right solar system size for your home depends on both the size of your house and your household’s daily electricity consumption. To maximize savings and ensure the best return on investment, it’s important to match your system size with your energy needs.
For more in-depth answers check out this simple solar system calculator and our comprehensive solar system sizing guide to better understand your specific needs.
Network Restrictions on Solar System Size
When choosing a solar system size, it’s important to understand that your local electricity network operator may place restrictions on the maximum size of the system you can install. These size limits can affect both the amount of solar energy you can generate and the amount of energy you can export back to the grid.
For example, most networks allow up to 5kW for single-phase homes and 10-30kW for three-phase connections, but these limits vary by state and network provider. Exceeding these limits might require extra approvals or technical assessments, and systems above certain sizes might not be eligible for feed-in tariffs.
To find out the specific solar system size limits for your area, check out our detailed guide: Solar System Size Limits: How Much Does Your Local Network Allow?
How Does Solar Power Save You Money?
First, it’s important to understand how installing residential solar panels on your home will actively reduce your electricity bill in order to assess if residential solar power is worth it. For now, we will set aside the environmental benefits of renewable solutions and focus on your electricity bill savings.
Offsetting Your Energy Consumption
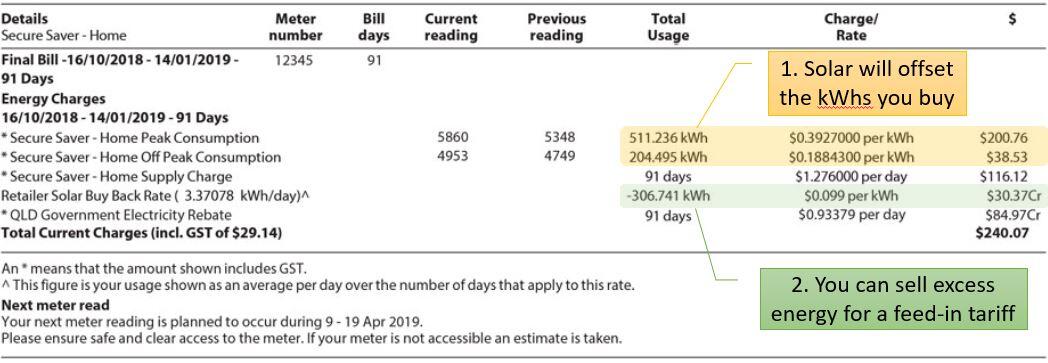
The primary way in which solar can help you tackle your energy costs is by reducing the amount of electricity you need to buy from your electricity retailer, which typically will cost between 20 cents and 50 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh).
A grid-connected solar system will prioritise solar energy and harmoniously supply any remaining energy needs from the grid.
A household can offset 25-75% of its energy usage with solar panels, depending on the typical patterns of when you are using electricity.
This offset percentage can get closer to 100% by installing a battery storage system.
Feed-in Tariff for Excess Energy
The sun determines the amount of energy generated by your solar panel system, not your energy consumption. During certain times, you can sell surplus energy back to the grid at a rate called a ‘feed-in tariff’.
These feed-in tariffs vary by state and which electricity retailer you are with. Typically you can find a feed in tariff between 2-12c per kWh.
Your ability to access a feed-in tariff is usually limited to a maximum solar system size – for a full explanation of what is possible state by state read this guide on comparing solar feed-in tariffs.
Installing solar will reduce the quantity of energy you buy, and you will notice an additional line item for the Feed-in credit on your electricity bill.
Options for Increasing Self-Consumption
As you can see above, it is much more valuable to ‘self-consume’ the solar power directly in your home, than it is to sell it back to the grid.
Increasing your self-consumption of solar energy will reduce your energy bills. To improve your return on investment you can consider applying a timer on common household appliances, such as:
- Electric hot water system
- Washing machine
- Dishwasher
- Swimming pool pump
- Underfloor heating system
You can buy programmable wall-socket timers from a hardware store for under $50 or an electrician can install one for you.
Compare quotes from up to 7 installers in your area now.
How Much Will I Save on my Electricity Bill?
Figuring out how much you’ll save on your electricity bill with solar requires a few key considerations.
First, you’ll need to determine the right system size for your home’s energy needs. Then, understand how much of that solar power you’ll use directly (self-consumption) and how much can be sold back to the grid through a feed-in tariff.
Working out how much a solar system will save you on your electricity bill requires some assumptions and an understanding of costs.
The Solar Choice advanced calculator will help you for free to look at different scenarios for your circumstances.
We have put together the below table which outlines some typical scenarios. We also have an easy to use calculator if your looking for some quick results.
How Much Do Home Solar Panels Cost?
| 3kW | 4kW | 5kW | 6kW | 7kW | 10kW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adelaide, SA | $3,540 | $4,010 | $4,440 | $5,000 | $5,790 | $7,570 |
| Brisbane, QLD | $3,840 | $4,370 | $4,820 | $5,300 | $6,290 | $8,250 |
| Canberra, ACT | $3,730 | $4,030 | $4,290 | $4,720 | $5,710 | $7,220 |
| Darwin, NT | $4,730 | $6,780 | $7,600 | $9,320 | $10,060 | $13,060 |
| Hobart, TAS | $4,620 | $5,400 | $6,030 | $6,750 | $7,240 | $10,830 |
| Melbourne, VIC | $4,030 | $4,480 | $5,000 | $5,480 | $6,320 | $8,360 |
| Sydney, NSW | $3,610 | $3,950 | $4,510 | $4,960 | $5,750 | $7,530 |
| Perth, WA | $3,200 | $3,570 | $3,970 | $4,760 | $5,410 | $8,470 |
| All | $3,910 | $4,570 | $5,080 | $5,790 | $6,570 | $8,910 |
Compare quotes from up to 7 installers in your area now.
What Extra Solar Power System Costs Should I Prepare for?
There are a range of additional costs that could apply to residential projects. Fortunately, as part of our online quote comparison service, we ask installers to advise what they would charge for the common extras that come up.
See the below table to see if any of these common items would apply to your home:
| Extra Cost | Range based on our price database | Reason |
| 2 Story Building | $200 to $800 | Need to use edge protection and hire a scissor lift |
| Tile Roof | $10-$50 per panel | More care needs to be taken with tile roofs, and racking is installed to the roof substructure under the tiles |
| Kliplok Roof Sheeting | $10-$50 per panel | Specialised non-penetrative clamps are required which are not required for other roof materials |
| Tilt Frames | $25 to $50 per panel | Usually only required if your roof is south-facing or completely flat to correct tilt or prevent dirt build up |
| Switchboard upgrade | $1000+ | No electrical contractor can install solar on a switchboard that isn’t to code without replacing it first |
| 3-phase properties | $500+ | Properties with a 3-phase power supply require compatible solar inverters that are more expensive than single-phase inverters |
Find out about Solar Panel Maintenance and Cleaning!
Beware of Cheap Solar Panels!
Inevitably once you start looking into solar you will start to come across some ‘too good to be true’ prices for solar – One Time Offer $2,999 for 6.6kW!
We recommend treating these companies with caution as usually they are making major sacrifices on customer servicing, product quality and installation procedures.
See this ABC coverage which covers some examples of what can go wrong.
They may be offering a 25-year + warranty on their residential solar install or solar products but that warranty is only valuable to you if the company is still around and there is a clear Australian warranty claim process.
We receive many phone calls from orphaned customers from years ago who are trying to contact Chinese factories to claim a warranty.
Ultimately if it looks too cheap, it probably is, and a too cheap solution will cost you more in the long run than a well-priced system.
Always do your research on the solar installation company and the products they are offering. See our article on the 5 questions you should ask your installer or email us or call us on 1300 787 273 if you need any help.
Expanding Your Solar System: Adding More Panels
If you’re thinking about adding more solar panels to your existing system, there are several factors to consider. This guide explains when and how to expand, whether you’re using an oversized inverter, have extra roof space, or plan to add battery storage. Expanding your system can increase energy production, save more on your electricity bills, and improve your return on investment. Learn more about adding panels to your solar system.
Calculate Your Roof’s Solar Potential
Use our Roof Exploration Tool to get a quick estimate of how many solar panels you can fit on your roof and the potential energy output. It’s a great way to understand your roof’s capacity before committing to a system size.
What About Solar Batteries?
The approximate cost of a solar battery currently stands at a bit over $1,000 per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of installed capacity.
This means a typical home battery would cost around $10,000. As we’ve demonstrated in-depth, the economic case for solar batteries is not as attractive as solar panels alone.
We expect that batteries will become viable for homeowners in the next 2-5 years, but that depends on manufacturers significantly increasing their scale of production and being able to pass on material discounts.
Solar Battery Size Calculator: What Size Do You Need?
This guide helps homeowners determine the correct solar and battery system size based on your daily energy consumption and system goals. It explains the importance of optimising your system for either maximising financial returns or increasing energy independence. The article includes a comprehensive table and calculator to assist users in selecting the appropriate solar and battery combination.
Understanding Australia’s Solar Rebate
Introduced in 2011, the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES) was introduced to support the uptake of renewable energy in Australia.
The SRES works by issuing Small-scale Technology Certificates (STCs) to homes & businesses that install systems under 100 kilowatts (kW) in terms of the DC Solar Panel capacity.
The STCs are officially created once a Clean Energy Council accredited Solar Installer has commissioned the system.
The Solar Installer sells the STCs either on the market themselves or via a broker/aggregator, meaning the end customer only needs to pay the difference.
How are STCs Calculated?
The STCs are based on the amount of renewable energy your system will generate before the end of 2030. You should note that STCs are calculated based on your postcode, the solar panel capacity of your system and the time left until 2030.
The length of time before 2030 changes annually on the 1st of January, so there will be a slight difference in the rebate value if you install your system after each new year.
Roughly speaking the rebate equates to around 30-35% of the total system cost.
Solar Payback Periods
Now you have the pieces to work out your return on investment (Upfront cost of solar, the amount of electricity bill you can offset and earnings from selling solar electricity at a solar feed-in rate)
As a quick guide, we have created the below table using some conservative assumptions for a typical residential scenario with a 5kW solar PV system:
Compare quotes from up to 7 installers in your area now.
How to Choose the Right Residential Solar Panels for Your House
As with many purchases, there are high-quality products, cost-effective products and cheap and nasty products that will cause more problems than benefits.
Solar is a long-term investment and given it requires accredited electricians to fix issues and replace equipment, our advice is to stick with the good brands.
While there is no substitute for good old-fashioned research, we have identified three easy tests to determine if a solar panel brand is ‘good’. Firstly you can look at Bloomberg NEF’s tier 1 ranking.
This ranking highlights the most financially secure solar panel manufacturers which is an indicator of whether they are likely to be around if you need to claim a warranty.
To further assess, you can verify if the solar panel brand is highlighted as a PV Evolution Labs’ annual ‘top performer’ in their independent tests.
Finally, through some googling, you should be able to establish whether the manufacturer has an Australian office and contact number. If your installer is no longer around this will be crucial if you need to claim a warranty directly.
To see a list of brands that meet these tests – head to our Solar Panels Comparison Page. We have also independently written a review on almost all Solar Panels, Inverters and Batteries on our Product Reviews Page.
How to Select a ‘Good’ Solar Installer
Selecting a good solar installer can be difficult. see our guide to choosing a good solar installer.
Over the last 16 years, we have vetted over 1,500 solar installation companies and curated a list of 400 to be part of our national quote comparison service.
Solar Choice’s Due Diligence Process for Home Solar Panel Installers
| Process | Minimum Requirements |
|---|---|
| 1. Verify company trading history via ABN Lookup | Minimum of 1 year trading history (ideally 5 years +) |
| 2. Check publicly listed reviews (Google reviews, Product Review, Trustpilot, etc.) | Minimum of 20 five-star reviews and an average rating of over 4 stars |
| 3. Check Clean Energy Council accreditation, Energy Contractors Licence, and Masters Electrician membership | Must be Clean Energy Council accredited for design and installation of grid-connected Solar PV systems |
| 4. Check products listed as standard offers on the Solar Choice comparison portal | No ‘cheap and nasty’ products; only reliable and high-quality products should be offered |
| 5. Request feedback from each customer 6 months after installation completion | Customer-reported issues must be very rare, and any identified issues should be resolved promptly and fairly |
While the vetting process above helps ensure you are choosing from high-quality, reliable solar installers, it’s still important to ask a few key questions before making your final decision. These questions will help you understand the specifics of the installation process, warranty, and long-term support.
Get In Touch With A Solar Choice Team Member
Still have questions?
Feel free to browse through the hundreds of useful articles on our site and blog or get in touch with us directly:
Call on Monday to Friday (9 am to 5 pm) on 1300 787 273
or
Email us anytime at sales@solarchoice.net.au
Frequently Asked Questions On Solar Systems
Are there different types of solar panels?
What is solar panel efficiency, and why does it matter?
What kind of warranties do solar panels offer?
What is the environmental impact of solar panels?
How do solar panels affect home aesthetics?
Can I buy solar panels online? Is it safe?
What maintenance do solar panels require?
Can solar panels handle extreme weather?
What should I consider when comparing solar panel brands?
Do solar panels from different countries perform differently?
- Why a big battery could be cheaper than a small battery with the federal rebate? - 19 June, 2025
- Heat Pump Costs – Solar Choice Price Index - 1 June, 2025
- Solar Panel Costs: Solar Choice Price Index | July 2025 - 1 June, 2025